- Qu Qingshan: Understanding the Five Distinctive Features of Chinese Modernization
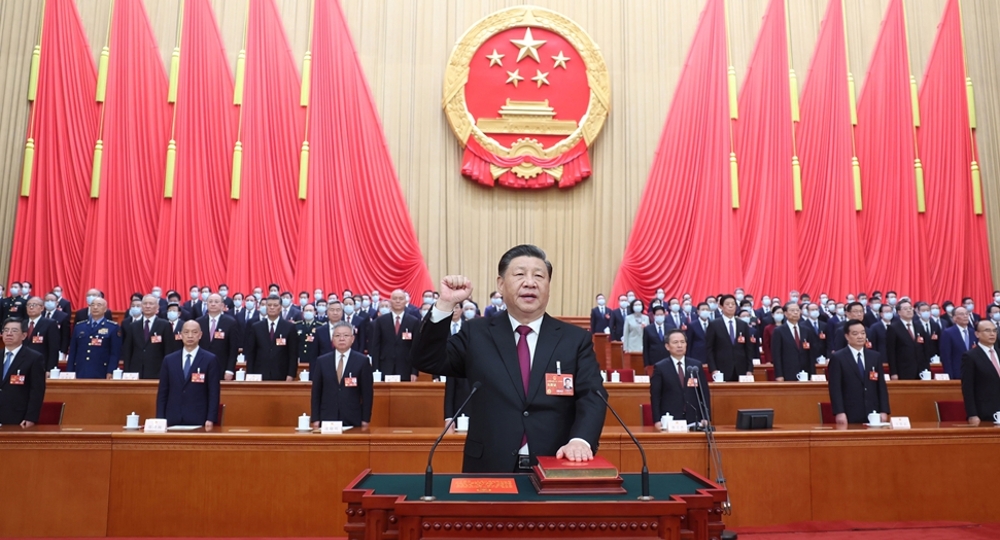
- Xi Jinping unanimously elected Chinese president, PRC CMC chairman
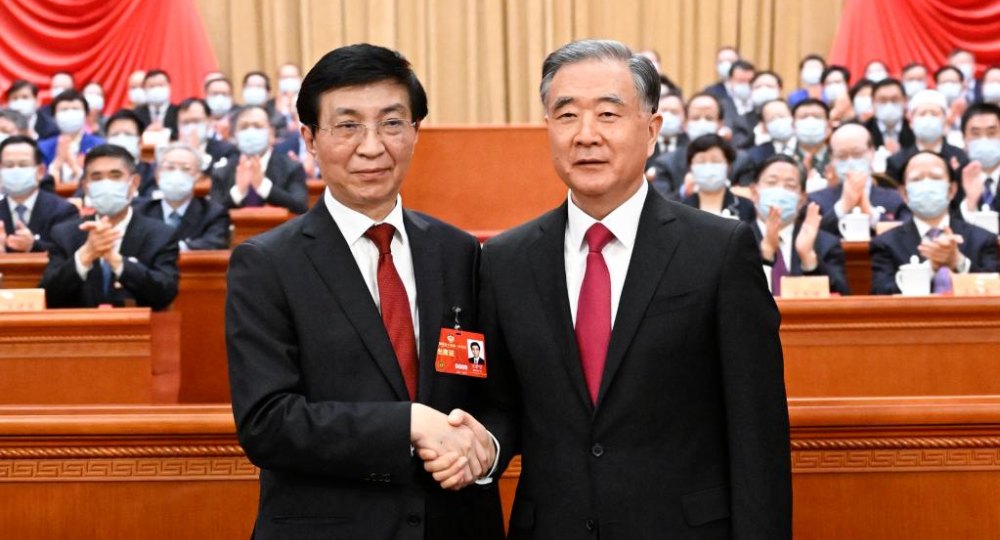
- Zhao Leji elected chairman of China's 14th National People's Congress Standing Committee
- Wang Huning elected chairman of China's top political advisory body
- More
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1924
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1928
- 1929
- 1930
- 1931
- 1932
- 1933
- 1934
- 1935
- 1936
- 1937
- 1938
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1942
- 1943
- 1944
- 1945
- 1946
- 1947
- 1948
- 1949
- 1950
- 1951
- 1952
- 1953
- 1954
- 1955
- 1956
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1960
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1964
- 1965
- 1966
- 1967
- 1968
- 1969
- 1970
- 1971
- 1972
- 1973
- 1974
- 1975
- 1976
- 1977
- 1978
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1982
- 1983
- 1984
- 1985
- 1986
- 1987
- 1988
- 1989
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1993
- 1994
- 1995
- 1996
- 1997
- 1998
- 1999
- 2000
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2004
- 2005
- 2006
- 2007
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2011
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2022
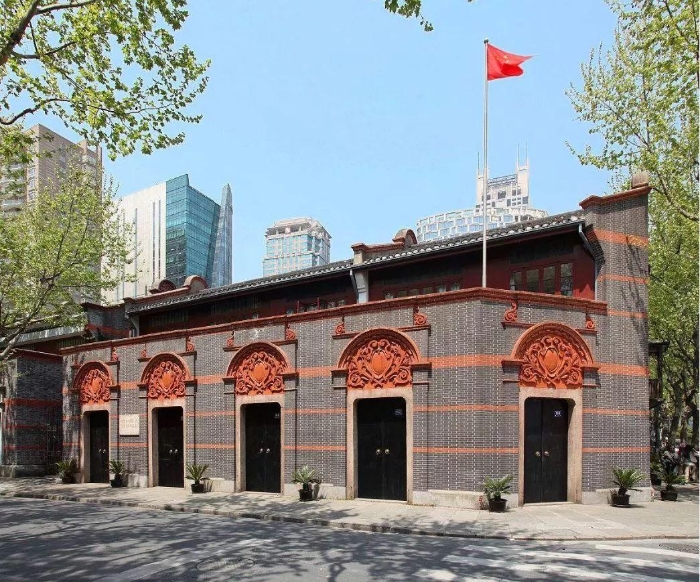
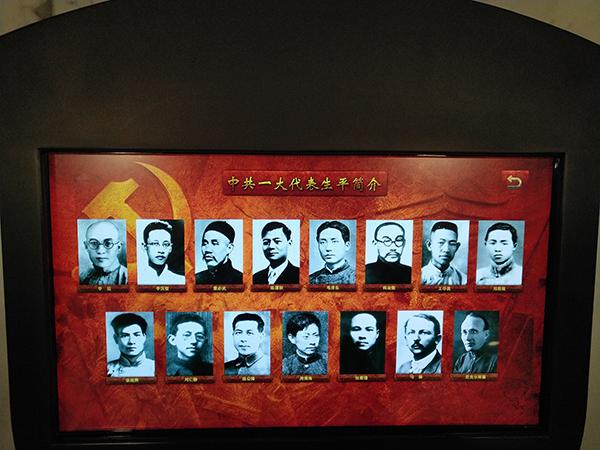
July 23-early August,1921
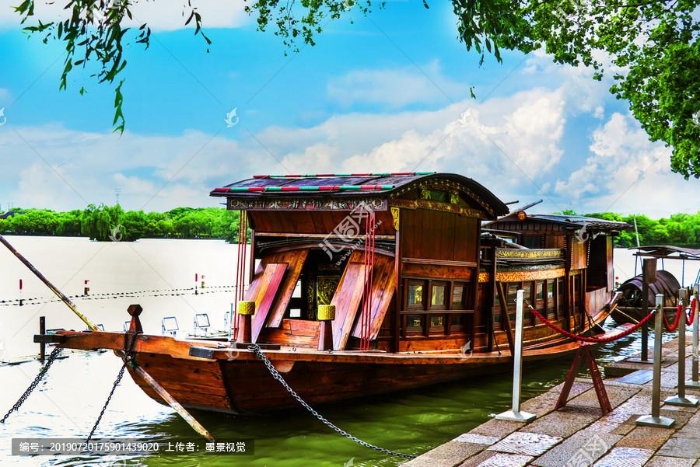
The First National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party was held in Shanghai. The 12 delegates to the congress were from the Communist groups in various parts of the country and from those in Japan. They were Mao Zedong, He Shuheng, Dong Biwu, Chen Tan- qiu, Wang Jinmei, Deng Enming (Shui nationality), Li Da, Li Hanjun, Zhang Guotao, Liu Renjing, Chen Gongbo and Zhou Fohai.There was another delegate named Bao Huiseng who was appointed by Chen Duxiu. These delegates represented more than 50 Party members. Two representatives from the Communist International, Malin and Nicolsky, also attended the congress. On July 30, the meeting had to be adjourned upon the sudden appearance of detectives on the scene. It was resumed on the final day on board a boat on Lake Nanhu in Jiaxing County, Zhejiang Province.
The central task of the congress was to discuss the question of officially founding the Chinese Communist Party. The congress adopted the Party programme and decided on the name of the Party as the Communist Party of China and on the objectives of the Party as follows: to overthrow the bourgeoisie by means of the revolutionary army of the proletariat, to rebuild the country by the labouring classes and to work for the ultimate elimination of differences between classes; to establish the dictatorship of the proletariat in order to attain the objective of class struggle, that is, the elimination of classes; and to abolish ownership by capitalists and establish ownership by the entire society through confiscating all the means of production. The Party programme enunciated explicitly the need to get the workers, peasants and soldiers organized and to disseminate communism and it recognized social revolution as the dominant policy of the Party. The programme also defined the organizational principle of democratic centralism and the discipline of the Party. The congress also adopted the “Resolution on the Present Tasks,” according to which the central task of the Party after its founding was to get the working class organized and provide guidance to the workers' movement and the Party should adopt a policy of independence to protect the interests of the proletariat in the struggles against the war- lords and bureaucrats and for freedom of speech, the press and assembly. A completely new-type and unified political party of the working class had thus emerged in China that took the realization of communism as its goal and Marxism-Leninism as its guide for action. The congress elected Chen Duxiu, Zhang Guotao and Li Da to form the Central Bureau with Chen serving as its secretary.
July 16-23,1922
The CPC held its Second National Congress in Shanghai, Twelve delegates attended the congress, representing 195 Party members.
The congress adopted and issued a historic declaration, Based on Lenin's theories on national and colonial questions and the examinations of the basic questions of the Chinese revolution made since the founding of the CPC, the declaration analyzed the world situation and the semi-colonial and semi-feudal nature of the Chinese society, expounded the character, motive force and targets of the Chinese revolution and formulated the minimum and maximum programmes of the Party. The objectives of the minimum programme, or the chief programme of the Party at the stage of democratic revolution, included eliminating internal disorder and overthrowing the warlords to achieve peace in the country; overthrowing oppression by world imperialism to gain complete independence for the Chinese nation; and unifying China as a genuine democratic republic. After these objectives were attained, further efforts should be made to prepare for the achievement of the objectives set by the maximum programme-“to establish the dictatorship by workers and peasants, eliminate the system of private ownership and gradually move into the communist society.” For the first time in modern China, the Second National Congress of the CPC explicitly set forth a programme of democratic revolution, opposing imperialism and feudalism, and thus it unequivocally charted the tasks and orientation for the people of various nationalities in China in their revolutionary struggles at the present stage.
For the benefit of carrying out the Party's programme for democratic revolution, the congress adopted the “Resolution on Democratic United Front,” calling on the workers and peasants throughout the country to rally under the banner of the CPC in their struggle, and at the same time to unite with all the revolutionary parties and the bourgeois democrats in the country to form a democratic united front in order to eliminate the feudal warlords, overthrow imperialist oppression and build an independent, truly democratic China.
The “Resolution on the Organizational Rules and Regulations of the Communist Party” adopted by the congress clearly defined the nature of the Party. It pointed out, "Our Communist Party is neither a Marxist academic society organized by intellectuals nor a utopian revolutionary organization of a few Communists who are divorced from the masses, It should be a political party fighting for the interests of the proletariat, a party of a large number of people of the proletariat who are imbued with the noblest revolutionary spirit and the vanguard of the proletariat in the revolutionary movement.” The resolution stressed that the CPC was the vanguard organization of the Chinese proletariat. The Constitution of the Chinese Communist Party adopted by the congress was the first constitution after the Party was founded. It contained specific provisions concerning requirements for Party members, the Party organizations at various levels and Party discipline.
Among others, the Congress also adopted the “Resolution on the Chinese Communist Party's Joining the Third Communist International,” the “Resolution on 'the Trade Union Movement and the Communist Party,”" the “Resolution on Women's Movement” and the “Resolution on the Juvenile Movement.” It elected the Central Executive Committee of the Party and Chen Duxiu chairman of the committee, and decided to publish a weekly The Guide as the organ of the Party, with Cai Hesen serving as the chief editor.
February 1,1923
The General Beijing-Hankou Railway Trade Union held a meeting in Zhengzhou to mark its inauguration. The Zhili warlord Wu Peifu ordered a ban on the trade union and sent out reactionary troops and policemen to occupy the seat of the General Trade Union. On February 4, over 20,000 workers of the Beijing-Hankou Railway went on strike, paralysing the 1,200-kilometre-long railway. On February 7, Wu Peifu, aided by imperialists, assembled more than 20,000 troops and policemen to suppress the striking workers in cold blood at Jiang'an, Zhengzhou, Changxindian and other railway stations. This became known as the “February 7 Massacre,” which shocked the country and the whole world Fifty workers were killed, more than 300 were wounded and over 40 were thrown into jail. Many workers' families were looted. Lin Xiangqian, a Communist Party member and president of the Jiang'an Branch of the Beijing-Hankou Railway Trade Union, and Shi Yang, also a Communis Party member and legal consultant of the General Beijing-Hankou Railway Trade Union, were executed. They displayed an indomitable spirit before the enemy and heroically laid down their lives. The great strike lasted until February 9, when the General Beijing-Hankou Rail- way Trade Union and the Workers' Union of Hubei Province asked the strikers to return to work in order to preserve the revolutionary strength.
June 12-20,1923
The CPC held its Third National Congress in Guangzhou. Attending the congress were 30-odd delegates who represented 420 Party members. According to the agenda, the congress was mainly to discuss the question whether the entire membership should join the KMT. It accepted the “Resolution on the Relationship Between the Chinese Communist Party and the Kuomintang” adopted by the Communist International on January 12 of the year and decided that all the CPC members join the KMT in the capacity of individuals for the benefit of establishing the united front of various democratic classes.
After the conclusion of the congress, Party organizations in various places carried out ideological work among the Party members to remove their doubts about joining the KMT. In the meantime, the Communist encouraged Dr. Sun Yat-sen and Liao Zhongkai to reorganize the KMT.
January 20-30,1924
Sun Yat-sen presided over the First National Congress of the KMT held in Guangzhou. The congress adopted an anti-imperialist and anti- feudal declaration drafted with the help of Communists, and decided on the Three Great Policies-alliance with Russia, cooperation with the Communist Party and assistance to the peasants and workers, thus developing the old Three People's Principles into the new Three People's Principles. The congress elected ten Communists, including Li Dazhao, Tan Pingshan, Mao Zedong, Lin Boqu and Qu Qiubai, as members or alternate members of the Central Executive Committee of the KMT. The headquarters of the KMT was also reorganized with Communists serving as director of the Organization Department and the Department of Peasants. The Department of Workers was actually led by Communists, too. Afterwards, most of the KMT local branches throughout the country were reorganized or set up with Communists or KMT Left-wingers comprising the backbone.
June 17-July 8,1924
The Communist International convened its Fifth Congress. Li Da-zhao, Wang Hebo, Peng Shuzhi and Liu Qingyang attended the congress as representatives of the CPC. The congress stressed the importance of the united front in the colonial countries and the need for the Communist Parties to maintain absolute and complete independence in negotiations with the upper stratum. It criticized the “Left” and Right opportunist tendencies found in united front work. Speaking on the questions of nations and colonies at the congress, Li Dazhao gave an account of imperialist activities in China and the development of China's national movement.
January 11-22,1925
The CPC held its Fourth National Congress in Shanghai. Twenty deputies representing 994 Party members attended the congress.The central item on the agenda was: to improve Party leadership over the daily-surging revolutionary movement and do propaganda, organization- al and mass work in preparation for the upsurge in the great revolution. The participants reviewed the Party's policies formulated and implemented since the Second Congress, reaffirmed the criticism of Right deviation in the work of the Party, made at the enlarged meeting of the Central Executive Committee in May the previous year, and decided on a number of new policies concerning cooperation with the KMT, the workers' movement and the peasants' movement. It was pointed out in the documents adopted at the congress that though an important instrument to China's national movement, the KMT was not the only force in the movement. The CPC must uphold a thorough programme of democratic revolution and maintain its independence both within and outside the KMT. It must expand the ranks of the Left, oppose the Right and win over the middle-of-the-roaders through ideological, organizational and mass propaganda work. While helping the KMT in practical struggles and in expanding its organizations, the CPC must persistently combat its compromising inclination. Having looked into combination of the workers' movement with the national movement, the congress stressed the need for the workers' movement to remain independent and keep growing in the midst of the national movement so as to gain leadership and make the national movement completely revolutionary. For this purpose, the working class must have powerful trade unions based on mass participation; more important, the organizations of the industrial workers must be brought under the guidance of the CPC. Regarding the workers' joining the KMT, the congress adopted different measures for different cases, emphasizing the need to combat bourgeois influence in the trade union movement and the scheme of KMT Right- wingers for a split. Having analyzed the role of the different classes in Chinese society in the national revolutionary movement, it called attention to the importance of leadership by the proletariat and of alliance between workers and peasants. The congress summed up the experience and lessons in the cooperation with the KMT since the previous year and worked out plans for unfolding mass movement. It also decided to set up and strengthen Party organizations throughout the country to meet the needs of great development in the revolution. The shortcoming of the Fourth Congress lay in that it failed to make a correct analysis of the Chinese national bourgeoisie, holding that it had not yet become an independent class and thus obscuring its role in the democratic revolution. As a result, it had either taken all the members of that class as enemies of the revolution, confusing in principle the difference between the two stages of the revolution, or neglected the activities of the national bourgeoisie in the revolutionary camp, thus writing off the task of the proletariat to contend for leadership with it. Moreover, the congress failed to work out a correct policy for the proletariat to win leadership, emphasizing only leadership over the mass movement to the total neglect of leadership over the government and the armed forces. It revised the Party Constitution and elected the new Central Executive Committee, which elected Chen Duxiu,Zhang Guotao,Peng Shuzhi,Cai Hesen and Qu Qiubai as members of the Central Bureau,with Chen Duxiu as general secretary.
May 30,1925
Students and representatives from other social strata in Shanghai demonstrated and made speeches against imperialism. The police of the International Settlement opened fire on them, killing a dozen of them and wounding many more. This became known as the “May 30 Massacre.” On the evening of the same day, the Central Committee of the CPC called another emergency meeting, at which it decided to set up an action committee and form united front of different classes to rouse the workers, students and merchants to stage strikes against imperialism.
September,1926
Mao Zedong published his article "The National Revolution and the Peasant Movement,” in which he pointed out that “the peasant question is the central issue of the national revolution" and that “the workers, students and middle and small merchants in the cities should launch a fierce attack on the comprador class and direct their attack on imperial- ism; leaders of the progressive working class and of all other revolutionary classes must be aware that the warlord and imperialist forces will never topple unless the peasants in the rural areas rise to overthrow the privileges of the patriarchal feudal landlord class.”
April 27-May 9,1927
The CPC held its Fifth National Congress in Wuhan. Eighty deputies attended the congress, representing over 57,900 Party members. The participants concentrated on discussing the Party's tasks at the critical moment.They accepted the resolution on the Chinese revolution adopted at the Seventh Enlarged Plenary Meeting of the Communist International Executive Committee. In view of what he had done in political struggles, they criticized Chen Duxiu for his Right deviationist mistakes as manifested in his neglect of the struggle with the bourgeoisie for leadership over the revolution. But they did not put forward any practical measures for correcting the mistakes. In the “Resolution on the Political Situation and the Party's Tasks” adopted at the congress, the Party made no concrete analysis of the situation in conformity with the reality,although it pointed out that since the May 30 Movement, it had “paid attention only to the struggle against imperialism and the warlords to the neglect of the struggle with the bourgeoisie for leadership over the revolution," so that it had failed to stop Chiang Kai-shek's betrayal. Moreover,in the resolution Chiang's betrayal was taken as betrayal by the bourgeoisie as a whole, as a result of which the national bourgeoisie was placed on a par with the comprador bourgeoisie and was regarded as the target of the revolution, too. And the KMT and the government in Wuhan, that were already under the control of Wang Jingwei and Tang Shengzhi,were regarded as the allies of the workers, the peasants and the petty bourgeoisie, and great hopes were pinned on Wang and Tang.The“Resolution on the Question of Land" adopted at the congress repeatedly stressed the importance of the agrarian revolution, maintain- ing that in the provinces “controlled by the revolutionary National Government,"the agrarian revolution could be carried out intensively. But it did not see that the force controlling the KMT and the government in Wuhan could not possibly be a supporter of the peasant movement. The congress emphasized the importance of winning leadership for the proletariat, setting up revolutionary democratic government and carry- ing out the agrarian revolution, but it did not work out effective and practical measures in the light of the critical situation in the revolution to solve the questions of how to win leadership by the proletariat over the revolution, how to lead the peasants in the agrarian revolution, what attitude to take towards the government and the KMT in Wuhan, and particularly how to build the Communist-led revolutionary armed forces.The congress elected the Central Committee composed of 29 members and 11 alternate members. The members of the Central Com- mittee then elected Chen Duxiu,Zhang Guotao,Li Weihan,Cai Hesen, Li Lisan,Qu Qiubai and Tan Pingshan as members, and Su Zhaozheng, Zhang Tailei,Chen Yannian and Zhou Enlai as alternate members, of the Political Bureau;Chen Duxiu, Zhang Guotao, Cai Hesen and Qu Qiubai(Li Weihan was added later) were elected members of the Political Bureau Standing Committee.Chen Duxiu was elected general secretary again.
August 1,1927
In accordance with the decision of the CPC Central Committee and under the leadership of Zhou Enlai, secretary of the Party's Front Committee, He Long, Ye Ting, Zhu De, Liu Bocheng and others, over 20,000 men of the National Revolutionary Army and other armed forces, who were either led or influenced by the Chinese Communist Party, staged an armed uprising in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, and occupied it. This uprising fired the first shot of armed opposition to the KMT reactionaries, ushering in a new period in which the Chinese Communist Party exercised independent leadership over revolutionary armed struggles and founded the people's revolutionary army. Beginning on August 3, the Front Committee led the army units to withdraw from Nanchang according to the original plan of the CPC Central Committee. Owing to lack of experience, the insurgent forces failed to join with the peasant movement in Jiangxi and other provinces and therefore they were besieged and defeated by superior enemy forces in late September and early October in the Chaozhou-Shantou area when they were moving southward to Guangdong. Part of the troops that had survived shifted to the Haifeng-Lufeng area to continue the fight, while the rest, commanded by Zhu De and Chen Yi, switched to southern Fujian and Jiangxi and the Guangdong-Jiangxi border area to engage in guerrilla operations there.
June 18-July 11,1928
With the help of the Communist International, the Sixth National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party was convened in Moscow. Attending the congress were 142 deputies, among whom 84 were full deputies (who had the right to vote), representing 130,000 Party members across the country. Qu Qiubai and Zhou Enlai made the main reports at the congress. Among other documents, the congress adopted the “Political Resolution,”pointing out that the Chinese society remained in nature a semi-colonial and semi-feudal society, that “the Chinese revolution at the present stage is in nature a bourgeois democratic revolution,” that the current political situation in China was one between two revolutionary high tides, and that the general task of the Party was, therefore, not to attack, but to win over the masses and prepare for insurrections. The congress worked out the revolutionary programme of opposing imperialism and feudalism, carrying out agrarian revolution and establishing the democratic dictatorship of workers and peasants and criticized “Left” and Right opportunism, especially putschist mistakes. The congress elected the Sixth Central Committee of the Party. At its First Plenary Session after the congress, the Sixth Central Committee elected Su Zhaozheng, Xiang Ying, Zhou Enlai, Xiang Zhongfa, Qu Qiubai, Cai Hesen and Zhang Guotao into its Political Bureau, with Guan Xiangying, Li Lisan, Luo Dengxian, Peng Pai, Yang Yin, Lu Futan and Xu Xigen as alternate members. It also elected the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau,with Su Zhaozheng, Xiang Zhongfa, Xiang Ying. Zhou Enlai and Cai Hesen as members.
January 14,1929
the Central Revolutionary Base Area
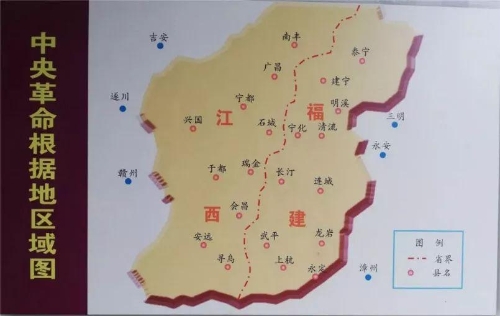
In order to break the third “joint suppression campaign” launched against the revolutionary base areas in the Jinggang Mountains by the enemy in Hunan and Jiangxi provinces and to solve the problem of the troops' supplies, Mao Zedong, Zhu De and Chen Yi led the main force of the Fourth Army of the Red Army to southern Jiangxi. Soon afterwards, they joined forces with the local Party organizations and armed units and set up the Southern Jiangxi and Western Fujian Revolutionary Base Areas. Later, the two base areas were linked together and became the Central Revolutionary Base Area.
May,1930
Mao Zedong invited representatives from different sectors in Xunwu County, Jiangxi Province, to a fact-finding meeting, and then wrote the “Survey of Xunwu.”At the end of October, he conducted rural social investigations in Yongfeng District of Xingguo County and wrote the "Survey of Xingguo."The large amount of work in rural survey done by Mao Zedong provided the scientific basis for the Party to formulate policies on the agrarian revolution, and at the same time, enriched and further developed Marxist thinking on investigation.
November 7-20,1931
The First National Congress of the Chinese Soviet was convened in Ruijin, which adopted the “Outline Constitution of the Chinese Soviet Republic,” the “Labour Law of the Chinese Soviet Republic,”the“Land Law of the Chinese Soviet Republic,”the“Decision Concerning the Economic Policies of the Chinese Soviet Republic” and other important documents, proclaimed the establishment of the Provisional Central Government of the Chinese Soviet Republic and elected the Central Executive Council consisting of 63 members. On the 25th,the Central Revolutionary Military Commission of the Chinese Soviet Republic (also known as the Revolutionary Military Commission of the Chinese Workers'and Peasants' Red Army) was formed with Zhu De as chairman and Wang Jiaxiang and Peng Dehuai as vice-chairmen. On the 27th, the Executive Council of the Central Government held its first meeting at which Mao Zedong was elected chairman of the Central Executive Council of the Chinese Soviet Republic, and Xiang Ying and Zhang Guotao vice-chairmen.
December,1932
In line with the decision of the Party Central Committee, the Shaanxi Provincial Party Committee redesignated the Shaanxi-Gansu guerrillas led by Xie Zichang and Liu Zhidan as the Twenty-sixth Army of the Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (there was only the Second Regiment). In November the following year, the Shaanxi-Gansu Border Area Special Committee made another decision to merge this main force of the Red Army with some guerrilla forces and form the Forty-second Division of the Twenty-sixth Army, which constituted the backbone force of the Shaanxi-Gansu Border Base Area.
June 30,1933
The Central Revolutionary Military Commission decided to make August 1st-the day of the Nanchang Uprising, the day on which the Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Red Army was founded, which was approved by the Provisional Central Government of the Chinese Soviet Republic on July 11. Thereafter, “August 1st”became the Army Day of the Chinese People's Liberation Army.
Middle October,1934
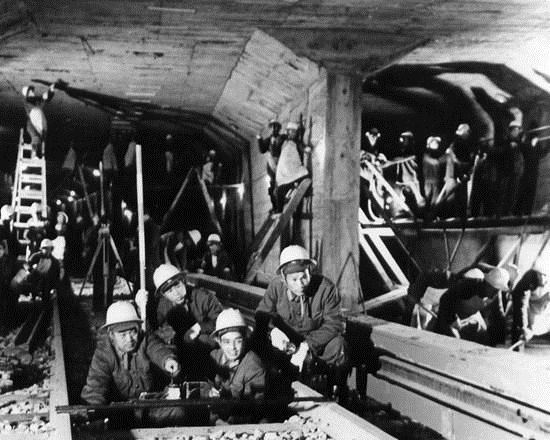
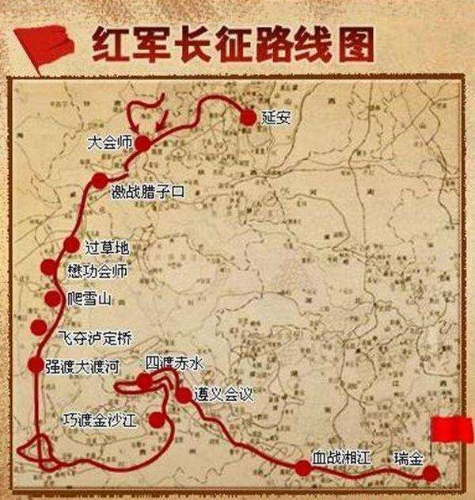
Xingguo, Ningdu and Shicheng counties in the Central Revolutionary Base Area fell into enemy hands one after another, dashing the hopes of thwarting the enemy's fifth “encirclement and suppression.” The main forces of the Central Red Army (the First Front Army) withdraw from the Central Revolutionary Base Area and shift to western Hunan to join forces with the Second and Sixth Army Groups. On the evening of the 10th, at the head of the main force of the Red Army along with the organs in the rear area, exceeding 86,000 men, the Party Central Committee and the General Headquarters of the Red Army left Ruijin, advanced towards western Hunan and began the Long March.
January 15-17,1935
An enlarged meeting of the Political Bureau of the Party Central Committee was convened in Zunyi. Attending the meeting were members of the Political Bureau Mao Zedong, Zhang Wentian, Zhou Enlai, Zhu De, Chen Yun and Bo Gu and alternate members Wang Jiaxiang, Liu Shaoqi, Deng Fa and He Kequan. The meeting was also attended by leading members of the Red Army Headquarters and various army groups Liu Bocheng,Li Fuchun,Lin Biao,Nie Rongzhen, Peng Dehuai, Yang Shangkun, Li Zhuoran as well as Deng Xiaoping, secretary-general of the Party Central Committee. Li De (Otto Braun), military adviser of the Communist International to China, and his interpreter Wu Xiuquan attended the meeting as observers. At the meeting the mistakes made by the Central Committee in guiding military operations during the cam- paign against the enemy's fifth “encirclement and suppression” and since the start of the Long March were exposed and criticized, Bo Gu's mistake in defending himself in his report for the failure of the campaign was repudiated, the “General Resolution on the Fight Against the Enemy's Fifth Campaign of 'Encirclement and Suppression”of the Central Com- mittee of the Chinese Communist Party was adopted and some necessary organizational adjustments were made. The resolution explicitly pointed out that the Red Army's failure in its campaign against the enemy's fifth “encirclement and suppression” and the heavy losses it suffered after leaving the Soviet areas should be attributed chiefly to the grave mis- takes committed by Bo Gu and Li De in their direction of the military operations. The meeting affirmed the fundamental operational principles formulated by Mao Zedong and others for the Red Army. It elected Mao Zedong member of the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau, deprived Bo Gu and Li De of their supreme military command, decided that Zhu De and Zhou Enlai, principal leaders of the Military Commis- sion of the Central Committee, remain in command of military affairs, and entrusted Zhou Enlai with the responsibility of making the final decision with regard to military affairs on behalf of the Party. In the course of the march after the meeting, the members of the Standing Committee divided up the work among themselves in the light of the spirit of the meeting,with Zhang Wentian holding responsibility in general in place of Bo Gu. After that, the Military Commission decided to set up the Front Headquarters with Zhu De as commander and Mao Zedong political commissar. Then, Mao Zedong, Zhou Enlai and Wang Jiaxiang formed the Group of Three to take charge of military opera- tions.Thus, the Zunyi Meeting ended the rule of Wang Ming's"Left” adventurism in the Central Committee and established the correct lead- ership of the new Central Committee represented by Mao Zedong.It was a meeting at which the CPC laid down its political line, principles and policies independently by applying the basic principles of Marxism- Leninism.Saving the Party and the Red Army at an extremely critical moment, it constituted a turning point on which hinged their survival in the history of the CPC and marked the maturity of the Party from its infancy.
December 9,1935
With national crisis deteriorating every day, several thousand patriotic students, led and organized by the CPC Provisional Working Committee in Beiping (Beijing), broke through KMT government's reign of terror and held a forceful demonstration for resistance against Japan and for national salvation. They shouted “Oppose the North China Autonomous Administration!” “Down with Japanese imperialism!” “Stop the civil war and unite against Japan!” and other slogans. On the 16th, over 10,000 students and citizens of Beiping held a mass rally at Tianqiao and staged a demonstration on a still larger scale. This movement, known as the
December 9th Movement, won the warm support of the people all over the country and brought about a new upsurge across the land for resistance against Japan and for national salvation.
October 22,1936
The three main forces of the Red Army joined forces. Since September 1935 when Zhang Guotao led the troops down south, the Fourth Front Army of the Red Army had wiped out large numbers of enemies, but it had also suffered heavy losses with its total number reduced by half. To avoid encirclement and attack by a strong enemy, it had to withdraw from the Tianquan, Lushan and Baoxing area in February 1936 and shift to the northeastern part of Xikang. In June, Zhang Guotao announced dissolution of the second “central committee.”In November 1935,the Second and Sixth Army Groups of the Red Army set off on the Long March from Sangzhi, Hunan. In June 1936,it reached the Ganzi area in Sichuan Province and joined forces with the Fourth Front Army that had arrived there earlier. In early July, they held a meeting to celebrate this event. On the 5th, the two army groups were reorganized, upon orders, as the Second Front Army of the Chinese Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, with He Long as its commander-in- chief and Ren Bishi political commissar. After the Second and Fourth Front Armies joined forces, thanks to the hard work done by the Central Committee to win him over, the struggle waged by Zhu De, Ren Bishi, He Long, Guan Xiangying and Liu Bocheng and the pressure exerted by the commanders and fighters of the Fourth Front Army in favour of a northward march to join the Central Committee, Zhang Guotao could not but agree to march northward along with the Second Front Army.
December 12,1936
The KMT's Northeast Army headed by Zhang Xueliang and its Seventeenth Route Army headed by Yang Hucheng, who had made many pleas to Chiang Kai-shek for stopping the civil war and uniting to fight Japan but were reprimanded instead, were compelled to stage the well-known Xi'an Incident by taking into custody Chiang Kai-shek who had come to Xi'an to make arrangements for “suppressing the Communists.” The CPC Central Committee correctly analysed the complicated situation and conducted repeated discussions before it worked out the principle for a peaceful settlement of the incident and sent Zhou Enlai, Qin Bangxian, Ye Jianying and others to Xi'an to take part in the negotiations. On the 24th, Chiang Kai-shek was forced to accept the terms of uniting with the CPC to resist Japan. Afterwards, Zhang Xueliang accompanied Chiang Kai-shek to Nanjing, where he was imprisoned by Chiang. The peaceful settlement of the Xi'an Incident served to promote another Kuomintang-Communist cooperation for united resistance to Japan and represented a turning point from civil war to national War of Resistance Against Japan.
July 7,1937
Evening of July 7, The Japanese aggressor troops launched an attack on the Chinese troops stationed at the Lugouqiao (Marco Polo Bridge) Bridge in Wanping County on the outskirts of Beiping. A section of the Chinese Twenty-ninth Army garrisoned there rose in resistance, thus ushering in the nationwide War of Resistance Against Japan.
May,1938
Mao Zedong published his “Problems of Strategy in Guerrilla War Against Japan” and “On Protracted War,” in which he comprehensively analyzed the era in which the Sino-Japanese war took place and the basic characteristics of Japan and China, expounded the general principle for the protracted war of resistance,the strategic role of the anti-Japanese guerrilla warfare and the strategies and tactics of the people's war, made a scientific prediction on the development of the anti-Japanese war, and refuted the “theory of national subjugation,” the “theory of quick victory” and the erroneous ideas of belittling the guerrilla warfare. As brilliant classics on solving the problems in the anti-Japanese war by dialectical materialism and historical materialism, these two articles enriched and further developed Marxist military science. June Soong Ching Ling founded the China Defense League in Guangzhou and Hong Kong respectively, with the aim of publicizing the Chinese people's anti-Japanese movement among people of various countries as well as the overseas Chinese, collecting medicine and other materials and introducing medical teams organized by international friends to take part in rescue work in the anti-Japanese base areas behind the enemy lines.
January 15-February 4,1939
The First Session of the First Assembly of Representatives of the Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia Border Region was convened. Attending the session were 145 representatives elected from among 2 million workers, peasants, intellectuals, merchants and enlightened gentry in the border region. The session heard reports on work made by various departments of the border region government and discussed problems concerning the building of the border region and the war of resistance. It adopted such important documents as the “Administrative Programme of the Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia Border Region in the Period of the War of Resistance" and elected a 15-member council of the border region government with Lin Boqu as chairman of the government.
August 20-early December,1940
The Eighth Route Army launched in north China the “Hundred-Regiment Campaign,” which was fought by 105 regiments. During the campaign, about 1,820 battles, big or small, were fought, killing and wounding 25,800 Japanese and puppet troops, capturing a great number of them, destroying 470 kilometres of railway, 1,500 kilometres of highway, 260 stations, bridges and tunnels, and a great number of fortifications and strongholds, and severely devastating the Zhengding-Taiyuan Railway and the Jingjing Coal Mines. On the part of the Eighth Route Army, 17,000 were killed or wounded, with fairly big losses suffered in some assaults on heavily fortified enemy strongholds in the second phase of the campaign. This campaign dealt heavy blows at the Japanese and puppet troops, fostered the people's confidence in victory in the war of resistance, enhanced the prestige of the CPC and the army under its leadership and encouraged people to persist in the war effort, check the adverse current of compromise and capitulation, and work for a turn for the better in the situation.
December 8,1941

The United States and Britain declared war on Japan after Japanese fascists launched a surprise attack against them on the Pacific Ocean, hence the outbreak of the Pacific War. On the 9th, the CPC issued a declaration with regard to the Pacific War, stating that it had finally become clear that the world was divided into the fascist front that unleashed the war of aggression and the anti-fascist front that waged the war of liberation. On the same day, the Chinese government formally declared war on Japan and at the same time on Germany and Italy. The outbreak of the Pacific War pushed the Second World War to its widest scale, and China's war of resistance and the war of the Allied Powers converged.
May 2,1942
The Party Central Committee held the Forum on Literature and Art at Yangjialing in Yan'an, at which Mao Zedong delivered important talks. He said the purpose of the forum was to exchange views and examine the relationship between work in the literary and artistic fields and the revolutionary work in general so as to ensure wholesome development of revolutionary literature and art, which would then facilitate other revolutionary work, the overthrow of the national enemy and the accomplishment of the task of national liberation. To achieve this objective, it was necessary to solve the problems of the class stand of writers and artists, their attitude, their audience and their study. The participants discussed the problems enthusiastically. On the 23rd, Mao Zedong made a conclusion in which he profoundly elucidated the basic orientation of revolutionary literature and art, i.e., to serve the people, analyzed the importance for literary and art workers to go among the workers, peasants and soldiers, apply theory to reality, study Marxism and remould their world outlook, and answered a number of controversial questions prevailing in the modern literary and art movement. Mao Zedong's talks at the forum not only served to promote the rectification movement in literary and art circles but also enhanced the awareness on the part of Party members and cadres of the need to study dialectical materialism and historical materialism and to remould their world outlook.
May 15,1943
In view of development of the anti-fascist war, the complicated conditions of struggle in each country and the need of the Communist Party in various countries to deal with their own problems independently, the Presidium of the Executive Committee of the Communist Inter- national made the “Decision on the Proposal for the Dissolution of the Communist International." The decision was made public throughout the world on the 22nd. On the 26th, the CPC Central Committee decided to fully agree to the decision, stating, “The Communist Party of China has obtained much help from the Communist International in its revolutionary struggle. But the Chinese Communists have long been able to make decisions completely on its own, on its political principles, policies and actions in the light of the concrete and particular conditions of the nation.” After the Communist International's formal dissolution on June 10, the CPC freed itself from its obligations to the Charter and Resolutions of the Communist International and from the influence of the Communist International.
October 10,1943
The CPC Central Committee decided that the Party's senior cadres should study afresh the history of the Party and the question of right and wrong concerning its line, bringing the rectification movement to the stage of summing up experience and arriving at a better understanding, which marked the end of the Party-wide rectification. This rectification movement was an education movement in Marxism-Leninism, an ideological revolutionary movement to overcome mistaken views with correct views and non-proletarian ideas with proletarian ideas, and also a great ideological emancipation movement to break the fetters of dogmatism represented by Wang Ming in the Party. It was of great significance in promoting integration of Marxism-Leninism with the concrete practice of the Chinese revolution and was a successful practice in correctly solving the question of building a proletarian political party.
September 15,1944
At the Third Session of the Third People's Political Council held in Chongqing, representative of the CPC Lin Boqu proposed abolition of the one-party dictatorship by the KMT, convening of a conference attended by various parties and establishment of a democratic coalition government. Later, the CPC raised to the KMT authorities again the proposal of establishing such a government in written form. On October 10, Zhou Enlai made a speech in Yan'an entitled “What is the Solution?” in which he further expounded the concrete steps and methods for convening an emergency meeting of representatives from various sectors of society to discuss state affairs and for establishing a democratic coalition government. The CPC's proposal concerning the democratic coalition government reflected the common desire and demand of the people of all strata in the country and aroused enthusiastic response from among the masses and democratic parties.
April 23-June 11,1945
The Seventh National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party was convened in Yan'an. Attending the congress were 547 full deputies and 208 alternate deputies, representing 1.21 million Party members. Mao Zedong presided over the congress. In his opening address he pointed out that China was confronted with a struggle between two prospects and two destinies and the Party's task was to strive with all its might for a bright future, a destiny of light, and against a dark future, a destiny of darkness. At the congress, he made the political report “On Coalition Government," the report on the situation and the ideological and political problems, the conclusion on the discussion of the political report and a speech on the question of election; Zhu De delivered the military report “On the Battlefield in the Liberated Areas” and the conclusion on the discussion of military problems; Liu Shaoqi made the report “On the Revision of the Party Constitution” and the conclusion on the discussion of the organizational question; and Zhou Enlai made an important speech “On the United Front.” Ren Bishi, Chen Yun, Peng Dehuai, Zhang Wentian, Chen Yi,Ye Jianying, Yang Shangkun, Peng Zhen and Nie Rongzhen also spoke at the congress. The congress adopted the political resolution, the military resolution and the new Party Constitution. It systematically summed up the Party's experience in leading the Chinese revolution in the past 24 years, profoundly expounded the basic theory of new-democracy, pointing out that the Party's line was to “boldly mobilize the masses and expand the people's forces so that, under the leadership of our Party, they will defeat the Japanese aggressors, liberate the whole people and build a new-democratic China.” The congress summed up the experience in armed struggle, united front and Party building and profoundly expounded these “three magic weapons" with which to carry out the new-democratic revolution, and the Party's three important styles of work-integrating theory with practice, forging close ties with the masses and conducting self-criticism. In the new Party Constitution adopted at the congress Mao Zedong Thought that integrated Marxist-Leninist theory with the practice of the Chinese revolution was made the guideline for all the Party's work. In accordance with the principle of developing democracy and strengthening unity and proceeding from the desire for unity, the participants carried out criticism and self-criticism against the mistakes made in the past and, adopting the conception that “one divides into two,” they patiently helped and explained things to errant comrades for the purpose of uniting and working together with them. The congress elected a new Central Committee. The Seventh Congress had gone down in history as a congress f unity and victory.
September 2,1945
Japanese Emperor and Government as well as the representative of the Japanese general headquarters signed the instrument of surrender. This crowned China's War of Resistance Against Japan and the Second World War with final victory. The War of Resistance Against Japan was a national liberation war in which the Chinese people won complete victory for the first time in a century-long struggle against foreign invaders and it was an important component of the anti-fascist world war.
Victory in the war of resistance was won through arduous and complicated struggle of the people of all nationalities throughout the country and at immense cost. According to statistics, over 21 million Chinese armymen and people were killed or wounded and the loss of property amounted to 60 billion U.S. dollars at least. During the eight years of the war of resistance, the Eighth Route Army, the New Fourth Army and other people's anti-Japanese armed forces led by the CPC fought 125,000 battles, wiping out 1,714,000 Japanese and puppet troops, capturing 694,000 arms of different kinds and 1,800 pieces of artillery. More than 600,000 commanders and fighters of the Communist-led armies lost their lives or got wounded and over 6 million people in the liberated areas were killed or wounded. Through the eight years of fighting, the people's revolutionary forces led by the CPC grew much stronger than before, the liberated areas covered an area of nearly one million square kilometres with a population of 100 million, and the main forces of the people's armies exceeded 1.2 million and the militia, 2.6 million. This laid a solid foundation for nationwide victory in the new-democratic revolution.
January 10,1946
The Political Consultative Conference attended by representatives of the KMT,the CPC, the Democratic League, the Youth Party and social celebrities was opened in Chongqing. Closed on the 31st, the conference adopted Agreement on Government Organization, Programme for Peace and National Reconstruction, Agreement on Military Affairs, Agreement on the National Assembly and Agreement on the Draft Constitution. The five documents, which in essence negated the KMT's one-party dictatorship and autocracy and its policy of civil war, were favourable to the people under the conditions prevailing at the time.
May 4,1946
The CPC Central Committee issued the “Directive on Settlement of Accounts and Reduction of Rents and the Land Question,” which was also known as the “May 4th Directive. It was changing the Party's policy of reduction of rent and interest carried out during the war of resistance to weaken feudal practices into one of “land to the tillers” to eliminate such practices.
June 30,1947
Liu Bocheng and Deng Xiaoping led the main force of the Shanxi-Hebei-Shandong-Henan Field Army, four columns totalling 130,000 men, in forcing the Yellow River from an area between Zhangqiuzhen and Linpu in southwestern Shandong to break through from the middle of the enemy's dumbbell-shaped battle array that extended from Shan-dong to northern Shaanxi, thus raising the curtain on the PLA's strategic offensive. At this point, the enemy's attacks on key sectors had not yet been completely smashed and the PLA was still far inferior to the enemy in terms of number and equipment. So, the shift in strategy represented a bold policy decision made by the CPC Central Committee after fully assessing the various factors that had a bearing on the war effort. Right after crossing the Yellow River, the Liu-Deng army waged the South-western Shandong Campaign, destroying nine and a half enemy brigades totalling 56,000 men. Then, they started a swift southward advance for 500 kilometres without a base rear to fall back on and arrived in the region of the Dabie Mountains towards the end of August.
April 30,1948
The CPC Central Committee published slogans for the May lst. International Labour Day, among which were “Fight all the way to Nanjing” and “All democratic parties, people's organizations and social celebrities immediately hold the political consultative conference to discuss and promote the convocation of the people's assembly and the establishment of a democratic coalition government.” On May 1, Mao Zedong, chairman of the CPC Central Committee, sent a telegram to Li Jishen, chairman of the Revolutionary Committee of the KMT and Shen Junru, member of the Standing Committee of the CDL, suggesting that a new Political Consultative Conference be held before anything else and also expressing the hope that the Revolutionary Committee of the MT and the CDL would work together with the CPC for these purposes. The CPC's suggestions were warmly received by the Revolutionary Committee of the KMT, the CDL, other democratic parties, people's organizations, overseas Chinese organizations and democrats without party affiliation. From August on, representatives from different quarters arrived in the liberated areas, and together with the CPC representatives they set preparing for the convocation of the new Political Consultative ference.
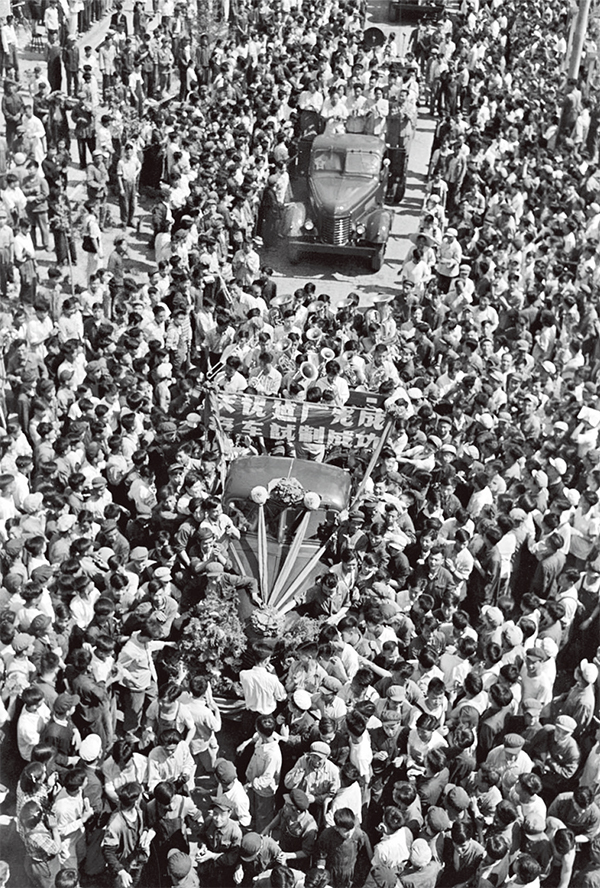
October 1, 1949

The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China was established.
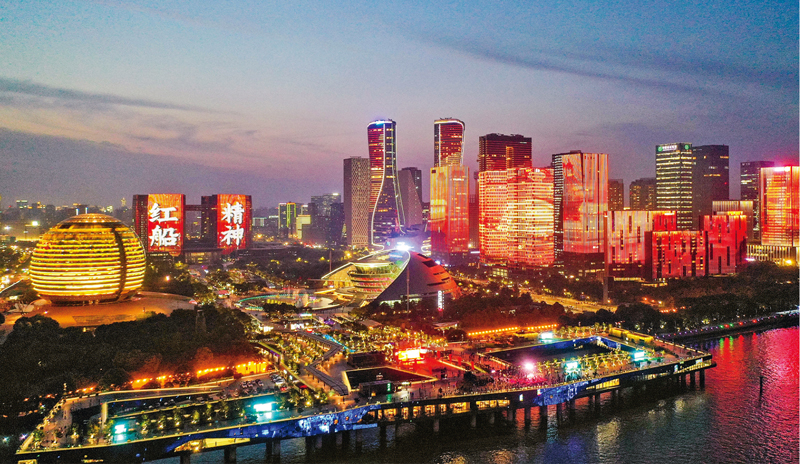
Previously from September 21 to 30, the 1st Plenary Session of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) was held, at which the Common Program of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, an interim constitution, was adopted. The Common Program stipulated that the state system of the People's Republic of China (PRC) was the people's democratic dictatorship led by the working class on the foundation of the alliance of workers and farmers, and its system of government was a people's congress system characterized by democratic centralism. The Session also passed the Organization Law of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference and the Organization Law of the Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. The Session decided that the PRC's capital was Beijing, which was to be renamed from Peiping; China's official calendar was to follow the AD system; the “March of the Volunteers" was to serve as the interim national anthem; and the Five-Starred Red Flag was to be the national flag, The Session elected Mao Zedong chairman of the Central People's Government, Zhu De, Liu Shaoqi, Soong Ching Ling, Li Jishen, Zhang Lan and Gao Gang vice-chairmen, and Chen Yi and 55 other members of the Central People's Government Committee. At 2 pm on October 1, the Central People's Government Committee held its first meeting and unanimously decided to accept the Common Program as the administrative policy of the government, and appointed Zhou Enlai as premier of the Administrative Council of the Central People's Government, Mao Zedong as chairman of the People's Revolutionary Military Commission and Zhu De as commander- in-chief of the People's Liberation Army. At 3 pm, a ceremony was solemnly held at the Tiananmen Square, Beijing to celebrate the founding of the Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. Mao Zedong proclaimed the establishment of the Central People's Government, followed by a grand military parade and a mass parade. On December 2, the 4th Meeting of the Central People's Government Committee was held, which decided that October 1 of each year was to be the national day of the People's Republic of China. The founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949 marked China's great leap from its millenia-old feudal autocracy to democracy of the people, a milestone of the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation since modern times. At that moment, the Chinese nation ushered in a new era of development and progress.
January 6

The Beijing Municipal Military Control Commission issued a notice, announcing the recovery of foreign military estate in Beijing and the requisition of barracks and other buildings. Tianjin, Shanghai and other places then followed suit. The rights of imperialist countries to station their military forces in the Chinese mainland were thus completely revoked.
May 23


The plenipotentiaries of the Central People's Government and the local government of Tibet signed in Beijing the Agreement on Measures for Peaceful Liberation of Tibet (known as the "17-Article Agreement"), proclaiming the peaceful liberation of Tibet. On October 26, the PLA entered Tibet and was stationed in Lhasa.
July 1

The Chengdu-Chongqing Railway, the first railway trunk line built entirely with domestically produced materials after the founding of the PRC, was completed and opened to traffic. By the end of 1978, railways such as Baoji-Chengdu, Yingtan-Xiamen, Baotou-Lanzhou, Lanzhou-Xinjiang, Chengdu-Kunming, and Hunan-Guizhou had been completed one after another.
April 18-24

Zhou Enlai led a Chinese delegation to the Asian-African Conference held in Bandung, Indonesia, which was attended by 29 countries. Sticking to the principle of “seeking common ground while reserving differences," the Chinese delegation, together with other participating countries, contributed to the success of the Conference by jointly advocating the “Bandung Spirit.” The Conference helped China open its door to Asian and African countries for extensive exchanges.
September 15-28

The 1st Session of the 1st NPC was held, marking the actual nationwide implementation of the system of the People's Congress. The meeting passed the Constitution of the People's Republic of China. Mao Zedong was elected chairman of the People's Republic of China and Liu Shaoqi chairman of the NPC Standing Committee. Zhou Enlai was appointed as premier of the State Council, and the establishment of the National Defense Commission was proposed with Mao Zedong as chairman.
March 1

The Central People's Government adopted the Election Law of the National People's Congress and the Local People's Congress of the People's Republic of China. After more than a year, over 214,000 organizations and institutions across the country held grass-root elections, with a total of over 323 million registered voters. More than 5.66 million deputies to the grass-root people's congresses were elected, and the local people's congresses at all levels were convened. On this basis, 1,226 deputies to the National People's Congress (NPC) were elected.
January 15

More than 200,000 people from all walks of life in Beijing had a meeting at the Tiananmen Square, celebrating the cooperativization of Beijing's agriculture and handicraft industry, as well as Beijing being the first in China to realize all-industry public-private joint management of capitalist businesses. By the end of the year, a decisive victory had been won throughout the Chinese mainland regarding the socialist transformation of private ownership of the means of production.
February 27


At the 11th (Enlarged) Meeting of the Supreme State Conference, Mao Zedong delivered a speech entitled “How to Handle the Contradictions among the People” (later renamed“ On the Correct Handling of Contradictions among the People”), in which he put forward the idea of distinguishing and correctly handling two different types of social contradictions and uniting the people of all nationalities to develop economy and culture and to serve the development of the cause of socialism.
End of August

The construction of the Great Hall of the People was completed, and it was known as one of the “Ten Great Constructions” built in the same year, with the other nine being the China Revolutionary History Museum, Chinese People's Revolutionary Military Museum, Cultural Palace of Nationalities, National Agriculture Exhibition Hall, Workers Stadium, Beijing Railway Station, Diaoyutai State Guesthouse, Minzu Hotel and Overseas Chinese Hotel.
April 9
The CPC Central Committee transmitted the Report on Adjusting Rural Labor Forces, and Streamlining and Sending Workers to Countryside drafted by the central five-man group for streamlining administration and managing labor forces. By June 1963, the staff of employees was cut down by 18.87 million across the country, and 26 million urban residents were resettled.
March 2
Zhou Enlai delivered the report On the Question of Intellectuals to the delegates attending the National Conference on Science Work and the National Forum on Creation of Drama, Opera and Children's Play, reaffirming that the overwhelming majority of the country's intellectuals belonged to the category of laboring people and emphasizing that it was necessary to give play to the roles of science and scientists in the course of socialist construction.
March 8 and March 22
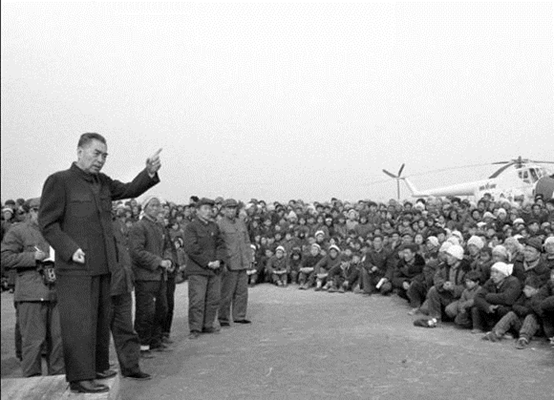

The area of Xingtai in Hebei Province was hit by two successive earthquakes with magnitudes of 6.8 and 7.2 on the Richter scale. Under the leadership of the CPC Central Committee, the State Council and the CPC Central Military Commission and thanks to the unstinting support from people around the country and the PLA, people of the disaster-stricken areas spared no efforts to carry out the earthquake relief work.
October 25

The 26th General Assembly of the United Nations passed the Resolution 2758 with a super majority vote, restoring all the lawful rights of the PRC in the United Nations and expelling forth with the representatives of Chiang Kai-shek from the United Nations and all the organizations related to it. On November 15, the delegation of the PRC for the first time took part in the General Assembly of the United Nations.
February 21-28

President Richard Nixon of the United States visited China. Before that, the US table tennis team visited China in April of 1971 after receiving an invitation; Henry Kissinger, a special assistant to the US president in national security, visited China twice in July and October of 1971. During his visit, Nixon met with Mao Zedong and held talks with Zhou Enlai. On February 28, China and the United States signed the Shanghai Joint Communiqué, which marked the beginning of the process of normalization of relations between the two countries.
October 12

The State Council approved and distributed the Opinions on the Enrollment Work of Institutions of Higher Learning in 1977 submitted by the Ministry of Education. It was decided that starting from that year, institutions of higher learning should adopt the methods of voluntary participation, unification of examination and excellence-based enrollment, and that the college entrance examination system that had been abolished during the "Cultural Revolution" should be restored. From November to December, around 5,700,000 people across the country took part in a nationwide unified examination organized by each province, autonomous region and municipality, with 273,000 people enrolled.
December 18-22

The 3rd Plenary Session of the 11th CPC Central Committee was convened. It criticized the erroneous "Two Whatevers" approach, fully recognized the need to have a full and precise understanding of the scientific system of Mao Zedong Thought, and highly praised the discussion on practice being the sole criterion for judging truth. It resolutely abandoned the use of the slogan--"grasp class struggle as the key link," and made a historic decision to shift the focus of the Party's and the country's work towards economic construction and launch reform and opening up to the outside world. It decided to improve the Party's system of democratic centralism, strengthen the leading organs of the Party establish the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection, and elect Chen Yun first secretary of the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection. The Session marked the CPC's re-establishment of the ideological, political and organizational line of Marxism, constituted a turning point of profound significance in the history of the Party since the founding of the PRC, and ushered in a great journey of reform and opening up as well as socialist modernization.
June 27

The 6th Plenary Session of the 11th CPC Central Committee adopted the Resolution on Certain Questions in the History of the Party since the Founding of the People's Republic of China, which justly reviewed major historical events of the Party over the 32 years following the founding of the PRC, especially the "Cultural Revolution," appraised the historical position of Mao Zedong in a matter-of-fact way, and fully expounded the great significance of Mao Zedong Thought as the guiding thought for the Party. On June 29, the Session elected Hu Yaobang chairman of the CPC Central Committee and Deng Xiaoping chairman of the CPC Central Military Commission.
September 30
Ye Jianying, chairman of the NPC Standing Committee, delivered a speech to reporters from the Xinhua News Agency, in which he further elaborated on the nine guidelines and policies concerning the return of Taiwan to the motherland and the realization of China's peaceful reunification.
September 1-11

The 12th CPC National Congress was convened. Deng Xiaoping proposed in his opening speech to integrate the universal truth of Marxism with the concrete realities of China for it to blaze a path of its own and build socialism with Chinese characteristics The Congress adopted the report entitled "Create a New Situation in All Fields of Socialist Modernization," which mapped out a strategic plan consisting of two major steps and set the objective of quadrupling the gross annual value of industrial and agricultural production by the end of the 20th century. The Congress also adopted the revised Constitution of the Communist Party of China and decided to set up the Central Advisory Commission.
February 20

China's first research base in Antarctica, the Great Wall Station built on the King George Island, was officially opened. And the Zhongshan Station, Kunlun Station and Taishan Station in Antarctica were completed afterwards.
May 23-June 6

Deng Xiaoping announced at the enlarged meeting of the Central Military Commission that China was determined to reduce the PLA forces by one million. The meeting marked a strategic shift in the guiding principles for military building.
September 28
The Resolution on Guiding Principles for Building a Socialist Society with an Advanced Culture and Ideology was adopted at the 6th Plenary Session of the 12th CPC Central Committee, which elaborated on the strategic position and the fundamental task of and the basic guideline for the construction of a socialist society with an advanced culture and ideology.
October 25-November 1


The 13th CPC National Congress was held. The report titled “Advance along the Road of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics was adopted at the Congress, which expounded the theory of the primary stage of socialism, put forward the basic line of the CPC on this stage, and formulated strategic plan involving three steps for the realization of China’s modernization by the mid-21st century. The Constitution of the Communist Party of China (Revised) was also passed at the Congress.
December 30
The CPC Central Committee formulated the Guidelines on Upholding and Improving the System of Multiparty Cooperation and Political Consultation under the Leadership of the CPC, which made clear that the system was a basic political system of China, and that “long-term coexistence, mutual oversight, sincerity and the sharing of both good and bad times” was the principle for the cooperation between the CPC and other political parties.
November 26

The Shanghai Stock Exchange, the first stock exchange in the Chinese mainland since the founding of the PRC, was established. On December 19, the Shanghai Stock Exchange was officially opened to the public. Afterwards, on July 3, 1991, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange was officially opened.
March 6
The Circular in Approval of the Establishment of the National High-Tech Industrial Development Zones and Related Policies and Regulations was issued by the State Council, which decided on listing Wuhan's Donghu New Technology Development Zone and other 25 development zones among the national high-tech industrial development zones after the approval of the establishment of the Beijing New Technological- Industrial Development Pilot Zone in 1988. By the end of 2018, China had set up 169 national high-tech industrial development zones including the Suzhou Industrial Park.
January 18-February 21


During the inspection tour of Wuchang, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Shanghai and other places, Deng Xiaoping delivered speeches and answered major questions that confused and constrained people for a long time. He pointed Out that in upholding the line, principles and policies formulated since the 3td Plenary Session of the 11th CPC Central Committee, it was essential to adhere to the principle of “one central task and two basic points.” The basic line should be adhered to for a hundred years with no vacillation: As for judging whether the road was capitalist or socialist, he said that the chief criterion should be whether it was favorable to developing the productive forces in a socialist society, to increasing the overall national strength of the socialist state and to raising the living standards of the people. Opportunities to accelerate development should be seized since development was the absolute principle. He specially emphasized that the proportion of planning to market forces was not the essential difference between socialism and capitalism. The essence of socialism was liberation and development of the productive forces, elimination of exploitation and polarization, and the ultimate achievement of prosperity for all. This talk was another declaration of emancipating the mind and seeking truth from facts that pushed forward the reform, opening up and modernization to a new Stage.
November 14

The Decision on Issues Concerning the Establishment of a Socialist Market Economy was adopted at the 3rd Plenary Session of the 14th CPC Central Committee. The Decision drafted a blueprint for establishing a socialist market economy and pointed out that the socialist market economy was an integral Part of the basic socialist system and that the purpose of establishing a socialist market economy was to let the market play a basic role in allocating resources under the state's macro-control. In addition, the Decision proposed to further transform the operating mechanisms of state-owned enterprises and create a modern corporate structure that met the requirements’ of the market and featured clearly established ownership, well-defined power and responsibility, separation of government administration and enterprise management, and scientific management.
January 11
The Decision on Further Deepening the Reform of the Foreign Trade System was released by the State Council. It pointed out that the objective of the reform was to unify policies, liberalize operations, equalize competition, let companies take full responsibility for profits and losses, combine industry and foreign trade, promote the agent system, and establish a new system that conformed to international norms.
September 28

The 5th Plenary Session of the 14th CPC Central Committee adopted the Proposal for Formulating the Ninth Five-Year Plan and the Long-Range Objectives through the Year 2010 for National Economic and Social Development. It proposed the implementation of two fundamental transformations of overall significance, namely, the transformation of the economic system from the old planned economy into the socialist market economy, and the transformation of the mode of economic growth from an extensive one to an intensive one. On the same day, Jiang Zemin addressed the Session and elaborated on 12 major relationships in socialist modernization, including the need to correctly balance reform, development and stability. On March 160 17, 1996, the 4th Session of the 8th NPC adopted The Ninth Five-Year Plan and the Long-Range Objectives through the Year 2010 for National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China.
October 10

The 6th Plenary Session of the 14th CPC Central Committee adopted the Resolutions on Certain Important Questions Concerning Further Promoting the Building of Socialist Culture and Ideology, which pointed out that a socialist society was one that developed and progressed comprehensively, and that socialist modernization was the coordinated integration of material progress with the building of socialist culture and ideology.
Midnight, June 30-Early Morning, July1

The Chinese and British governments held a ceremony for the handover of the sovereignty of Hong Kong and declared China's resumption of its exercise of sovereignty over Hong Kong. The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) of the PRC was officially established. Following the handover ceremony, the ceremony for the establishment of the HKSAR of the PRC and the swearing-in of HKSAR officials was held. The PLA Hong Kong Garrison was to perform their defense duties from 00:00, July 1, 1997.
September 12-18

The 15th CPC National Congress was held. It adopted the report entitled "Hold High the Great Banner of Deng Xiaoping Theory and Comprehensively Advance the Cause of Building Socialism with Chinese Characteristics in the 21st Century." The Report laid stress on the historical position and guiding significance of Deng Xiaoping Theory, put forward the basic line for the primary stage of socialism, and explicitly affirmed that upholding and improving the basic economic system whereby socialist public ownership was dominant and economic entities under diverse ownership forms developed side by side was a 166 basic economic system of China at the early stage of socialism. It also emphasized the importance of law- based governance and the need to build a socialist country under the rule of law, and clearly defined the cross-century development goals of reform and opening up, and modernization. The Congress adopted the Constitution of the Communist Party of China (Revised) that included Deng Xiaoping Theory as a guiding ideology of the CPC along with Marxism- Leninism and Mao Zedong Thought.
Mid-June-Early September
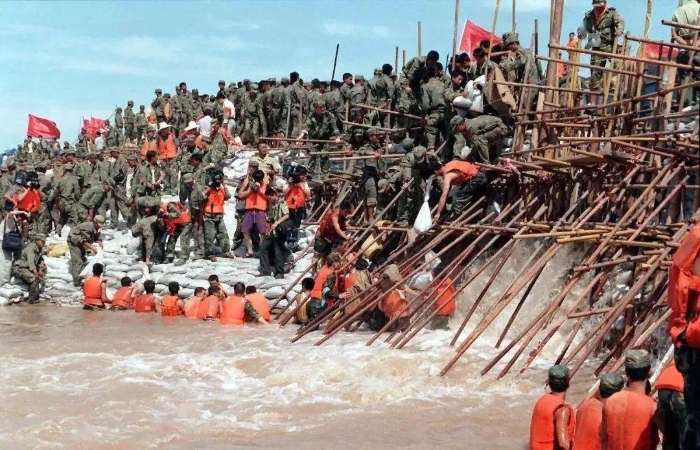

The Yangtze River in southern China and the Nenjiang River and Songhua River in northern China experienced the worst flooding in the recorded history. Under the leadership of the CPC Central Committee, the State Council and the Central Military Commission, the whole Party, the army and people of all ethnic groups acted in unison and achieved a full victory in the fight against foods.
Midnight, December 19-Early Morning, December 20

The Chinese and Portuguese governments held a ceremony for the handover of Macao and declared China's resumption of its exercise of sovereignty over Macao. The Macao Special Administrative Region (MSAR) of the People's Republic of China was officially established. Following the handover ceremony, the ceremony for the establishment of the MSAR of the PRC and the swearing-in for MSAR officials was held. The PLA Macao Garrison performed their defense duties there beginning at 0:00 on December 20, 1999.
October 11

The 5th Plenary Session of the 15th CPC Central Committee adopted the Proposal for Formulating the Tenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development. It pointed out that the Chinese people had generally lived a fairly comfortable life, and China would enter a new stage of building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and accelerate socialist modernization from the beginning of the 21st century. Jiang Zemin addressed the Plenary Session saying that the general strategy for China's economic development at the beginning of the 21st century was to make a strategic adjustment of the economic structure, promote the two fundamental transformations and ensure the sustainable, rapid and sound development of the national economy. On March 15, 2001, the 4th Session of the 9th NPC approved the Outline of the Tenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China.
On the same day, Jiang Zemin, in his speech after the closing ceremony of the 5th Plenary Session of the 15th CPC Central Committee, elaborated on the tasks of safeguarding the stability of Xinjiang, including combating ethnic separatism, religious extremism and terrorism, on the basis of its history and reality. He stressed that maintaining the stability and development of ethnic minority and border areas was vital for the political and overall situation, which was of great significance to the long-term stability of the country with regard to both society and politics.
July1

In his speech delivered at the meeting celebrating the 80th anniversary of the founding of the CPC, Jiang Zemin summarized the outstanding achievements and practical experience of the CPC over the past 80 years and expounded the Important Theory of Three Represents. He stressed that since the beginning of the reform and opening up, new changes had taken place in the composition of China's social strata, and there had emerged entrepreneurs and technical personnels of private scientific and technological enterprises, managerial technicians working in foreign-funded enterprises, self-employed personnels, private entrepreneurs, practitioners for intermediary 182 organizations, freelancers and other people. They were also to be seen as builders for the cause of socialism with Chinese characteristics.
November 10

The 4th WTO (World Trade Organization) Ministerial Conference held in Doha of Qatar deliberated on, and then reached a unanimous decision to approve China's accession to the WTO. On December 11, China officially became a member of the WTO, entering a new stage of opening up.
November 8-14

The 16th CPC National Congress was held. The report entitled "Building a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects and Creating a New Situation for Socialism with Chinese Characteristics" adopted in the meeting proposed the goals for building a moderately prosperous society in all respects, and expounded the basic requirement for putting the Important Theory of Three Represents into full effect. The Congress adopted the Constitution of the Communist Party of China (Revised), established the Important Theory of Three Represents as the guiding ideology of the CPC along with Marxism-Leninism, Mao Zedong Thought and Deng Xiaoping Theory, and incorporated it into the Constitution of the Communist Party of China.
Spring

China suffered from an intense outbreak of SARS never seen before. Under the strong leadership of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, the whole Party and the people across the country made persistent efforts to prevent and control SARS while striving to promote economic growth, achieving a great victory for SARS prevention and control. On July 28, Hu Jintao delivered a speech at the National Conference on SARS Prevention and Control, and stated that from a long-term point of view, it was essential to further study and promote the coordinated development of the economy and society.
October 14

The 3rd Plenary Session of the 16th CPC Central Committee adopted the Decision on Certain Issues Concerning Improving the Socialist Market Economy. It clearly identified the major task of improving the socialist market economic system, and proposed that a development outlook that put people first and aimed at comprehensive, balanced and sustainable development must be upheld to promote an all-round development of the economy, society and people.
July 28
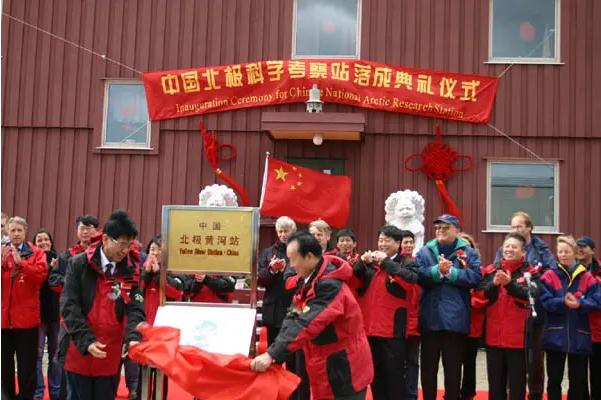
The Yellow River Station, China's first Arctic scientific research station, was completed and put into operation in Ny Alesund on the Spitsbergen Islands, Norway. China officially became an Observer State of the Arctic Council on May 15, 2013.
September 16-19eptember
The 4th Plenary Session of the 16th CPC Central Committee was held. It adopted the Decision on Strengthening the Party's Governing Ability, approved Jiang Zemin's resignation as chairman of the CPC Central Military Commission and appointed Hu Jintao as chairman of the CPC Central Military Commission.
April 29

Hu Jintao, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, held an official meeting with Chinese Kuomintang chairman Lien Chan. After the meeting, both parties released the Common Vision of Peaceful Development across the Taiwan Straits. This was the first meeting between the top leaders of the two parties in 60 years.
October 11

The 6th Plenary Session of the 16th CPC Central Committee adopted the Decision on Several Major Issues of Building a Harmonious Socialist Society. The Decision stipulated that social harmony was the essence of socialism with Chinese characteristics and emphasized that it was imperative to build a harmonious socialist society in accordance with the general requirements for democracy and the rule of law, equity and justice, honesty and fraternity, vigor and vitality, stability and order, and harmony between man and nature, so as to promote the coordinated development of social and economic, political and cultural construction.
October 15-21

The 17th CPC National Congress was convened. The report entitled “Hold High the Great Banner of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics and Strive for New Victories in Building a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects” adopted by the Congress fully expounded the content, the essence and the fundamental requirements of the Scientific Outlook on Development. It, clearly defined development as the essence of the Scientific Outlook on Development, making putting people first its core, comprehensive, balanced and sustainable development its fundamental requirement and overall consideration its fundamental approach. The Congress also approved the Constitution of the Communist Party of China (Revised) with the inclusion of the Scientific Outlook on Development. It was at this Congress that ecological construction was put forth for the first time as a new requirement for attaining the goal of building a moderately prosperous society in all respects.
July 1

At the celebration marking the 90th anniversary of the CPC, Hu Jintao stated that after 90 years of struggle, creation and experience, the Party and the people must cherish, persist in and carry forward the following great achievements: the forging of the road of socialism with Chinese characteristics, the establishment of the system of theories of socialism with Chinese characteristics and the building of the socialist system with Chinese characteristics.
November 8-14

The 18th CPC National Congress was convened. The report titled “Firmly March on the Path of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics, and Strive to Complete the Building of a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects” specified the goal of building a moderately prosperous society in an all-round way and deepening reform and opening up, and it also stipulated the content of and relations between the path of socialism with Chinese characteristics, the system of theories of socialism with Chinese characteristics and the socialist system with Chinese characteristics. The Congress approved the Constitution of the Communist Party of China(Revised),making the Scientific Outlook on Development, together with Marxism-Leninism, Mao Zedong Thought, Deng Xiaoping Theory and the Important Theory of Three Represents the theoretical guidance of the Party and part of the Constitution.
March 23

Xi Jinping delivered a speech at the Moscow State Institute of International Relations in Russia, stressing that human beings were increasingly part of a human community with a shared future. He called on all countries to jointly step up the establishment of a new international relationship with win-win cooperation as the core. On September 28, 2015, Xi Jinping attended the general debate of the 70th UN General Assembly at the UN Headquarters in New York and delivered a speech, proposing to jointly build a new partnership of win-win cooperation and a human community with a shared future. On January 18, 2017, Xi Jinping attended the High-Level Meeting on Discussing and Building a Human Community with a Shared Future at the Palais des Nations in Geneva and delivered a keynote speech, in which he advocated working together to build a human community with a shared future, and sticking to the principle of "dialogue and consultation, joint contribution and shared benefits, win-win cooperation, mutual learning and low-carbon development," so as to build an open, inclusive, clean, and beautiful world that enjoyed lasting peace, universal security, and common prosperity.
November 19-21

The 1st World Internet Conference was held in Wuzhen, Zhejiang Province, identifying Wuzhen as the permanent site of the World Internet Conference. Xi Jinping delivered a keynote speech at the opening ceremony of the 2nd World Internet Conference on December 16, 2015, stressing that cyberspace was the common space of activities for mankind and calling for a joint building of community with a shared future in cyberspace.
September 3

An assembly and a military parade were held to commemorate the 70th anniversary of the victory of the Chinese People's War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression and the World Anti-Fascist War. Xi Jinping reviewed the troops and delivered a speech, announcing that China would cut troop numbers by 300,000.
October 24-27
At the 6th Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee, the Code of Conduct for Intraparty Political Life under New Circumstances and the Regulations of the Communist Party of China on Internal Oversight were adopted. The Session established the core status of General Secretary Xi Jinping in the CPC Central Committee and the whole Party, and called on all comrades in the Party to closely unite around the CPC Central Committee with Comrade Xi Jinping at its core, to firmly establish consciousness of the need to maintain political integrity, think in big-picture terms, uphold the leadership core, and keep in alignment, and to unswervingly uphold the authority and centralized, unified leadership of the CPC Central Committee.
May 14-15

The 1st Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation was held in Beijing. Xi Jinping attended the opening ceremony and delivered a keynote speech, stressing that the Belt and Road should be built into a road to peace, prosperity, openness, innovation and civilization. From April 25 to 27, 2019, the 2nd Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation was held in Beijing. Xi Jinping was present at the opening ceremony and gave a keynote speech, emphasizing the need to follow the principle of achieving shaved growth through discussion and collaboration, adhere to the concept of openness, greenness and cleanliness, strive to achieve high standards, benefit people's livelihood and sustainable goals, and promote the high-quality development of the Belt and Road. In the six years since Xi Jinping proposed the Belt and Road Initiative in 2013, the volume of China's trade with countries along the Belt and Road totaled more than US$6 trillion and its direct investment in these countries exceeded US$90 billion. A general interconnection framework consisting of six corridors, six routes and multiple countries and ports had been put in place and a large number of cooperation projects have been established, with successful implementation of all the projects proposed at the 1st Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation.
October 18-24

The 19th CPC National Congress was convened. It adopted the report entitled “Secure a Decisive Victory in Building a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects and Strive for the Great Success of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era," which came to the major political conclusion that socialism with Chinese characteristics had entered a new era, the principal contradiction facing Chinese society had evolved into the contradiction between unbalanced and inadequate development and the people's ever-growing needs for a better life, established the historical position of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, formed the basic policy of upholding and developing socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era, and set the goal of securing a decisive victory in fully build a moderately prosperous society in all respects and embarking on a journey to building a modern socialist country. The Congress adopted the Constitution of the Communist Party of China (Revised) that included Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, along with Marxism-Leninism, Mao Zedong Thought, Deng Xiaoping Theory, the Important Theory of Three Represents, and the Scientific Outlook on Development, as the Party's guiding ideology.
February 26-28

The 3rd Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee was held. The Session adopted the Decision on Deepening the Reform of the Party and the State Institutions and the Plan for Deepening the Reform of the Party and the State Institutions. On March 17, the 1st Session of the 13th NPC approved the plan for institutional restructuring of the State Council. On July 5, 2019, a conference reviewing the deepening of reform of the Party and state institutions was convened, at which Xi Jinping pointed out that deepening the reform of the Party and the state institutions was a systematic and holistic reconstruction of the organizational structure and management mechanism of the Party and the state institutions, which provided a strong institutional guarantee for improving and developing the socialist system with Chinese characteristics and advancing the modernization of China's governance system and capacity.
May 15-22

The 1st Conference on Dialogue of Asian Civilizations was held in Beijing. At its opening ceremony, Xi Jinping delivered a keynote speech titled “Deepen Exchanges and Mutual Learning among Civilizations for an Asian Community with a Shared Future," calling for the need to respect each other and treat each other as equals, uphold the beauty of each civilization and the diversity of civilizations in the world, stay open and inclusive, draw on each other's strengths and advance with the times and explore new ground in development in an effort to create an even better tomorrow for civilizations in Asia and beyond.
October 1,2019
China put on a grand
celebration, followed by a military parade and mass pageantry at
Tian'anmen Square on Oct 1, the National Day, to mark the 70th
anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China (PRC).
September 8

China held a meeting Tuesday morning in Beijing to commend role models in the country's fight against the COVID-19 epidemic. President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, presented medals to recipients of the Medal of the Republic and the national honorary title at the Great Hall of the People. Xi also delivered a speech at the meeting, attended by about 3,000 people. China has made major strategic achievements in the battle against COVID-19, demonstrating the notable advantages of the CPC leadership and the country's socialist system, the great strength of the Chinese people and the Chinese nation, the profound heritage of Chinese civilization, and the nation's sense of responsibility as a major and responsible country, Xi said. He called for transforming the virus-fighting spirit into tremendous strength to build a modern socialist country and achieve national rejuvenation. The meeting was presided over by Li Keqiang and attended by other senior leaders: Li Zhanshu, Wang Yang, Wang Huning, Zhao Leji, Han Zheng and Wang Qishan.
February 20

Xi Jinping, general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee, on Saturday stressed studying the Party's history as the CPC celebrates its centenary this year. Xi, also Chinese president and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made the remarks while delivering an important speech at a key meeting to launch a campaign on Party history learning and education among all Party members. Calling the campaign a major decision made by the CPC Central Committee, Xi urged efforts from all CPC members to study the Party's history, understand its theories, do practical work and make new advances, thus to embark on a new journey in high spirit to fully build a modern socialist China and to welcome the Party's centenary with outstanding achievements. Xi said the CPC has always attached great importance to the study and education of its history. He stressed the vital necessity of launching the campaign as the CPC stands at a critical juncture where the timeframes of its two centenary goals converge. Xi urged Party committees at all levels to earnestly implement the arrangements made by the CPC Central Committee on the campaign. "Our Party's history is a history of continuously adapting Marxism to the Chinese context," Xi said. He called for educating and guiding the whole Party to learn from its "extraordinary" past so as to understand how Marxism has profoundly changed China and the world. He also called for efforts to equip the whole Party with the latest achievements in its theoretical innovation, and to use the theories to guide its practice and advance its work. Throughout its 100-year history, the CPC has been of one mind with the people, breathed the same breath as the people, and shared weal and woe with the people, said Xi. With people's trust and support, the CPC is invincible in the face of any obstacles, Xi said, adding that it is the duty of the CPC to cement the unity of 1.4 billion Chinese people to create an unstoppable force to push forward the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
July 1
Xi
Jinping, general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC)
Central Committee, Chinese president and chairman of the Central
Military Commission, delivers an important speech at a ceremony marking
the centenary of the CPC in Beijing, capital of China, July 1, 2021.
(Xinhua/Li Xueren)
BEIJING,
July 1 (Xinhua) -- Xi Jinping, general secretary of the Communist Party
of China (CPC) Central Committee, Chinese president and chairman of the
Central Military Commission, started delivering an important speech at a
ceremony marking the centenary of the CPC on Thursday.
Nov. 8 to 11
The sixth plenary session of the 19th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC), held in Beijing from Nov. 8 to 11, has adopted a landmark resolution on major achievements and historical experience of the Party over the past century.
It is the century-old Party's third resolution on historical issues. Seventy-six years have passed since its first resolution on historical issues and 40 years since the second.
Noting that learning from history is a vital characteristic in Chinese culture, Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee, has stressed that the Party has consistently attached great importance to reviewing its historical experience.
April 8
A ceremony was held at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing on the morning of April 8 to honor those who have made outstanding contributions to the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics and Paralympics.
President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, delivered a speech.
Xi said that a great cause nurtures a great spirit, and a great spirit promotes a great cause. The participants in the Games cherished the opportunity presented by the great era, and in the process of bidding, organizing and hosting the Games, they have created the spirit of bearing in mind the big picture, being confident and open, rising to the challenges, pursuing excellence, and creating a better future together. Xi called for carrying forward the spirit of the Games, and forging ahead more confidently and more determinedly toward the second centenary goal and toward the Chinese Dream of national rejuvenation.
May 10
A ceremony marking the 100th anniversary of the founding of the Communist Youth League of China is held at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing, capital of China, May 10, 2022.Xi, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, made the remarks on the ceremony.
Xi urged CYLC members to be patriotic and innovative, while not being misguided or intimidated by difficulties.
CYLC members shall also be hardworking and willing to make selfless contributions, said Xi, adding that they should promote virtue, perform good deeds and observe discipline.
-

Advance the Rejuvenation of the Chinese Nation Through a Chinese Path to Modernization
-

Striving for High-Quality Development
-

The Great Changes in the First Decade of the New Era
-

Building a High-Standard Socialist Market Economy
-

Making Basic Elderly Care Available to the Entire Elderly Population
-

Common Prosperity in Daicun Village
-

Turning Stony Deserts to Green
-

Powering a Better Life and a Beautiful China
-

"Who Doesn't Say Our Hometown Is Good"
-

A Model Village Called Haojiaqiao